Lethal Bronzing Disease: A Threat to Palm Trees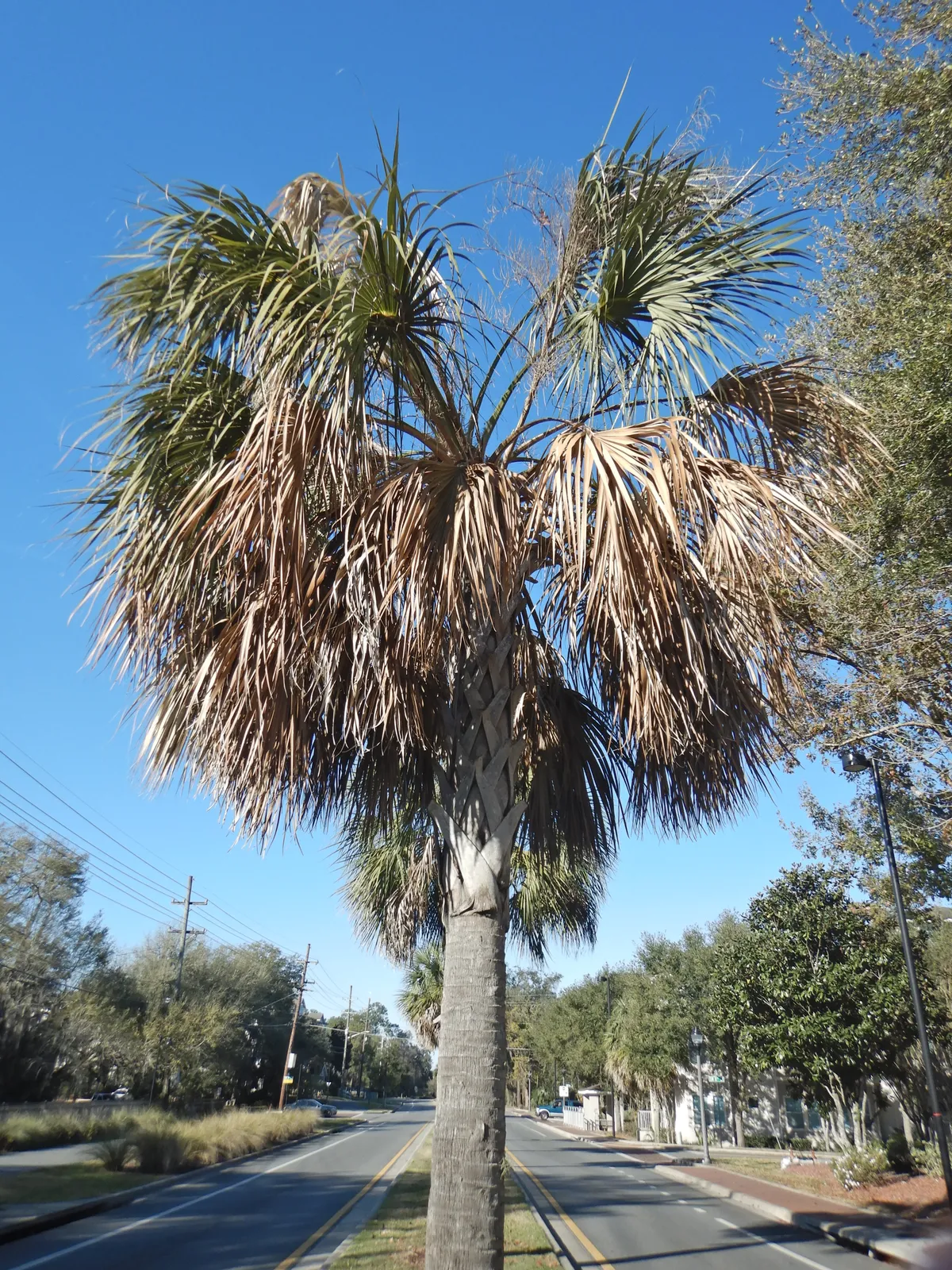
Lethal Bronzing Disease poses a significant threat to palm trees, causing widespread damage and potential tree loss. This article aims to provide a simplified overview of what Lethal Bronzing Disease is, its causes, symptoms, and measures to manage and prevent its spread. By understanding this disease, we can take proactive steps to protect our beloved palm trees and maintain the beauty of our landscapes.
What is Lethal Bronzing Disease?
Lethal Bronzing Disease, also known as Texas Phoenix Palm Decline (TPPD), is a lethal bacterial infection primarily affecting various palm tree species. It is caused by the bacterium called “Candidatus Phytoplasma palmae.” The disease is transmitted by a tiny insect called the “Haplaxius crudus” or the “American palm cixiid,” which feeds on the sap of infected palm trees and carries the bacteria to healthy trees.
Causes of Lethal Bronzing Disease:
The primary cause of Lethal Bronzing Disease is the introduction of the bacteria into healthy palm trees by infected insects. These insects are known as vectors and can spread the disease from tree to tree. Factors such as warm climates, increased vector populations, and the presence of susceptible palm tree species contribute to the spread and severity of the disease.
Symptoms of Lethal Bronzing Disease:
Identifying the symptoms of Lethal Bronzing Disease is crucial for early detection and management. Look for the following signs:
- Discoloration: Affected palm trees exhibit an overall bronze or reddish-brown discoloration of the fronds (leaves), starting from the lower canopy and gradually progressing upwards.
- Wilting and Decline: The fronds become necrotic, drying out and wilting from the tips inward. Eventually, the affected fronds die and hang down, giving the tree a “skirted” appearance.
- Premature Fruit Drop: Palm trees infected with Lethal Bronzing Disease may experience premature dropping of their fruit clusters.
- Stunted Growth: Infected palms may show stunted growth, with reduced or distorted new growth.
Managing and Preventing Lethal Bronzing Disease:
While there is no known cure for Lethal Bronzing Disease, certain measures can help manage and prevent its spread:
- Early Detection: Regularly inspect palm trees for any signs of discoloration, wilting, or other symptoms. Early detection allows for prompt action and reduces the risk of further spread.
- Vector Control: Implement measures to control the population of insect vectors, such as using insecticides or beneficial predator insects.
- Remove Infected Trees: Infected palm trees should be promptly removed and destroyed to prevent the bacteria from spreading to healthy trees.
- Plant Resistant Species: When planting new palm trees, choose species that are resistant to Lethal Bronzing Disease.
- Professional Assistance: Consult with certified arborists or tree care experts who can provide guidance on disease management strategies and recommend appropriate treatments.
Lethal Bronzing Disease poses a significant threat to palm trees, potentially causing irreversible damage and tree loss. By familiarizing ourselves with the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate management and prevention measures, we can actively protect our palm trees and preserve the beauty of our landscapes. Regular monitoring, early intervention, and professional advice are crucial to mitigating the impact of Lethal Bronzing Disease and ensuring the health and longevity of our cherished palm trees.