Annosus root disease: understanding and managing this tree threat

Annosus root disease is a common fungal infection that poses a significant risk to the health and longevity of trees. This article aims to provide a straightforward explanation of what Annosus root disease is, its causes, symptoms, and some practical management strategies. By understanding this disease, we can take proactive steps to protect our trees and preserve our green spaces.
What is Annosus Root Disease?
Annosus root disease, also known as Heterobasidion root rot, is caused by the fungus Heterobasidion annosum. It primarily affects coniferous trees, such as pines, firs, spruces, and hemlocks. The fungus enters the tree through wounds or damaged roots and gradually spreads, causing decay and weakening the tree’s root system.
Causes of Annosus Root Disease:
The Heterobasidion annosum fungus thrives in moist environments, especially in areas with poor soil drainage. It spreads through fungal spores that can be carried by wind or water. Logging activities, tree wounds, improper pruning, and the presence of infected trees in proximity can facilitate the spread of the disease.
Symptoms of Annosus Root Disease:
Detecting the symptoms of Annosus root disease is crucial for early intervention. Look for the following signs:
- Reduced Growth: Infected trees may exhibit stunted or slow growth, with sparse foliage and shorter annual needle length.
- Root Decay: The disease attacks the tree’s root system, leading to the decay of the inner wood. Affected roots appear dark and spongy.
- Crown Discoloration: The tree’s crown may show yellowing or thinning, indicating a decline in overall health.
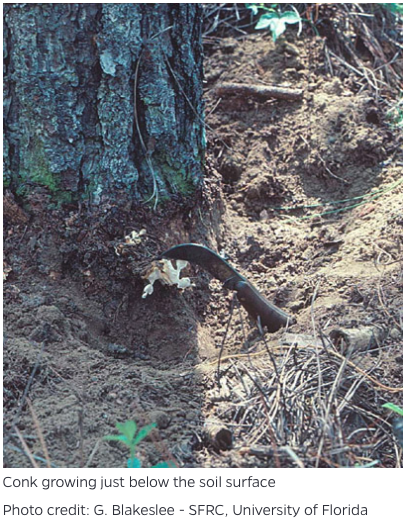
- Presence of Fruiting Bodies: During the late summer and fall, shelf-like fruiting bodies (conks) may appear on the lower trunk or roots. These conks have a flat, plate-like appearance with a brownish color.
Managing Annosus Root Disease:
While complete eradication of Annosus root disease is challenging, proactive management can help limit its impact. Consider the following strategies:
- Promote Tree Health: Maintaining proper tree care practices, such as regular watering, appropriate fertilization, and mulching, helps strengthen the tree’s natural defenses against diseases.
- Preventative Measures: When conducting logging or tree removal activities, promptly treat fresh wounds with a registered fungicide to minimize the risk of infection.
- Improve Soil Drainage: Ensure good soil drainage to discourage fungal growth. Avoid excessive irrigation and amend soil with organic matter to enhance its structure.
- Remove Infected Trees: Infected trees should be removed and properly disposed of to prevent further spread of the disease.
- Consult a Professional: If you suspect Annosus root disease or need assistance with management strategies, consult an experienced arborist or tree care professional.
Annosus root disease can significantly impact the health and stability of our cherished trees. By familiarizing ourselves with its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate management practices, we can mitigate the risks and safeguard our arboreal ecosystems. Regular monitoring, early intervention, and professional guidance are key to minimizing the effects of Annosus root disease and ensuring the longevity and vitality of our treasured trees.