Transplanting Trees: A Guide to Successfully Relocating Nature’s Giants

Transplanting trees is a process that offers numerous benefits, allowing us to preserve mature trees, redesign landscapes, and create thriving green spaces. However, it is important to recognize that not all trees are suitable candidates for transplantation. In this blog post, we will explore the art and science of transplanting trees, including when it may not be advisable to proceed with the process.
Certain factors may make a tree unsuitable for transplantation, including:
Age and Size- Older, more mature trees have extensive root systems that may be difficult to transplant successfully. Very large trees can also present logistical challenges due to their weight and size.
Health and Condition- Trees that are already in poor health, weakened by disease, or heavily infested by pests may not survive the stress of transplantation. Prioritize the health of the tree and consult with an arborist to assess its viability.
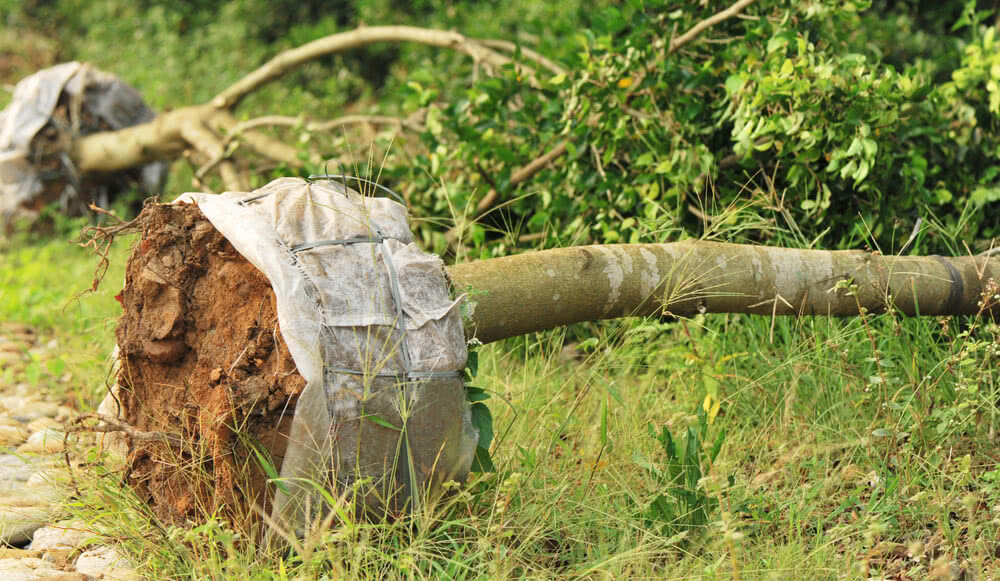
Root System Damage- If the tree’s roots have been significantly compromised, such as by construction or severe root pruning, the tree may not have the necessary root structure to support successful transplantation.
Transplanting trees may not be feasible or advisable under certain site limitations, such as:
Unsuitable Soil Conditions- If the soil in the new planting location is fundamentally incompatible with the tree’s requirements, it may not be possible to transplant the tree successfully. Some species have specific soil pH, moisture, or nutrient requirements that must be met for healthy growth.
Space Constraints- Trees that require a large area to thrive may not be suitable for transplantation if the new site lacks sufficient space for their roots to spread and canopy to grow.
Timing is crucial when it comes to tree transplantations. In certain situations, it may be best to avoid transplanting trees:
Active Growth Periods- Transplanting trees during their active growth periods, such as spring and early summer, can increase stress and reduce the chances of successful establishment. It is generally recommended to transplant during dormant periods, such as early spring or late fall, when the tree is less actively growing.
Cost and Resources-
Transplanting trees can be a complex and costly process that requires specialized equipment, skilled personnel, and ongoing care. It is essential to consider the financial implications and available resources before proceeding with transplantation.
While transplanting trees can offer numerous benefits, it is important to recognize that not all trees are suitable candidates for transplantation. Factors such as age, size, health, root system damage, site limitations, and seasonal considerations must be carefully evaluated before embarking on a tree transplantation project. Consulting with a certified arborist or tree care professional is highly recommended to assess the feasibility and potential success of the transplantation process. Remember, preserving existing trees through appropriate care and maintenance is often the best approach to ensure their longevity and contribution to the environment.