Co-Dominant Stems in Trees: Are They Dangerous?
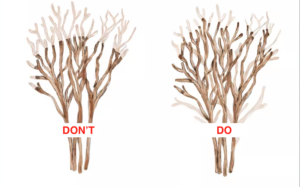
 Have you ever noticed some trees with two or more main branches that seem to be competing for attention? These are called co-dominant stems, and they can affect a tree’s structure and safety. In this article, we’ll explore what co-dominant stems are, why they can be dangerous, and how to address them to ensure the health and well-being of trees.
Have you ever noticed some trees with two or more main branches that seem to be competing for attention? These are called co-dominant stems, and they can affect a tree’s structure and safety. In this article, we’ll explore what co-dominant stems are, why they can be dangerous, and how to address them to ensure the health and well-being of trees.
Understanding Co-Dominant Stems:
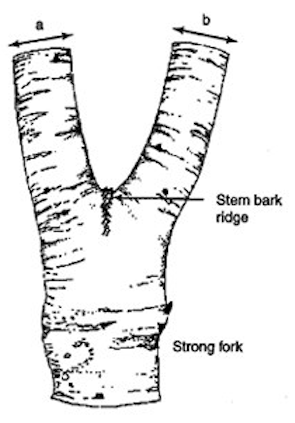
Co-dominant stems occur when two or more main branches of similar size and strength grow upward from a tree’s trunk. Instead of having a clear central leader, these stems develop in close proximity to each other, often forming a tight “V” or “U” shape. While some tree species naturally grow this way, co-dominance can also be the result of poor pruning practices or certain environmental factors.
The Dangers of Co-Dominant Stems:
Co-dominant stems can pose a risk to the tree’s structural integrity. The union between the stems tends to be weak, especially when the bark gets trapped between them, forming what is known as included bark. As the tree grows and matures, this weak union becomes a potential weak point. During storms, heavy winds, or under the weight of snow or ice, the tree may be more prone to splitting or breaking at the co-dominant stem junction.
Preventing Potential Hazards:
It’s important to address co-dominant stems early on to prevent potential hazards. Proper pruning techniques can help promote a strong and healthy tree structure. Here’s what you can do:
- Consult an Arborist: It’s best to consult a professional arborist or tree care specialist who can assess the tree and recommend the best course of action. They have the expertise to determine the severity of co-dominant stems and the appropriate pruning methods.
- Select a Dominant Stem: The arborist will identify the most suitable candidate for a central leader among the co-dominant stems. This stem should be structurally sound and have the best potential for healthy growth.
- Pruning: With careful precision, the arborist will remove or reduce the competing co-dominant stems. This process allows the selected dominant stem to develop into a central leader, strengthening the tree’s structure over time.
- Regular Maintenance: Ongoing tree care and maintenance, such as regular pruning and inspections, will help monitor and manage any potential issues that may arise in the future.
Co-dominant stems in trees can be dangerous if not properly addressed. Their weak union and potential for splitting or breaking pose risks to the tree’s structure and surrounding property. However, with the help of a professional arborist, the hazards associated with co-dominant stems can be managed through careful pruning and ongoing tree maintenance. By taking proactive measures, we can ensure the health and safety of our trees, promoting a beautiful and thriving urban landscape.