Invasive Species Explained: The Different Categories
Invasive Species Explained: The Different Categories
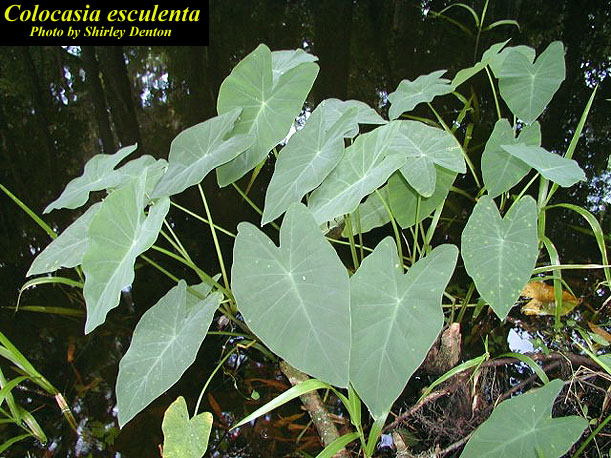
An invasive species is a plant or animal that lives in an area they do not naturally exist in. These species are introduced to new ecosystems, and in some cases can damage the ecosystems they are introduced to. Depending on the environment that it was introduced to it may have the ability to spread rapidly and compete with the naturally occurring (native) species, this will cause ecological and economic harm. Based on the effect on the ecosystem they are introduced to will determine which category they belong in.
Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council (EPPC) is an organization established to track and manage the invasive plants in Florida’s natural areas. EPPC categorizes the invasive plants into two categories. The following information is from the Florida EPPC website;
CATEGORY I
“Invasive exotics that are altering native plant communities by displacing native species, changing community structures or ecological functions, or hybridizing with natives. This definition does not rely on the economic severity or geographic range of the problem, but on the documented ecological damage caused.
CATEGORY II
“Invasive exotics that have increased in abundance or frequency but have not yet altered Florida plant communities to the extent shown by Category I species. These species may become ranked Category I, if ecological damage is demonstrated.”
The Break Down of Sub-Categories
Invasive species may also be sub categorized based on the environment they affect as well. It’s important to note that some invasive plant species can fall into multiple categories depending on their behavior and impact.
Noxious weeds:Invasive plants that are considered harmful to the environment they are introduced to. They can be harmful to human health, or even the economy. They are regulated by federal or state laws in order to try to prevent them from spreading and overtaking an ecosystem. Some laws may require landowners to control or eliminate them completely.
Ecological invaders:Invasive plants that disturb natural ecosystems by outcompeting native plants and reducing biodiversity. They may cause significant damage to a natural ecosystem’s health by changing the chemistry and water cycle.
Agricultural invaders:Invasive plants that can affect the production of crops. They may alter the soil fertility or introduce diseases. They can have a severe impact on the agricultural industry, as well as the economy.
Horticultural invaders:Invasive plants that are often used in landscaping and garden design. These plans can potentially escape cultivation and spread to natural areas and reduce biodiversity.
Aquatic invaders:Invasive plants that grow in bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, or swampy marshlands. They can affect the water quality, reduce water flow and circulation and even reduce aquatic biodiversity.